Example of firewall configuration to allow only certain clients to access the Internet when switching to the backup channel
One of the standard ways to use a router is when it is connected by cable to the main Internet channel and also uses a backup connection via a 5G/4G/3G modem.
The logic of this setup is as follows: the router constantly checks the availability of the Internet on the primary channel (Ethernet connection to an ISP), and if there is no connection, it automatically switches to using the backup Internet connection via a 5G/4G/3G modem. Then, when the Internet connection is restored on the primary connection, the router will return to working with the main channel. However, in this scheme, all devices that were connected to the router will switch to the backup connection. And since the backup connection we are considering is through the mobile operator's network, the question of traffic savings arises.
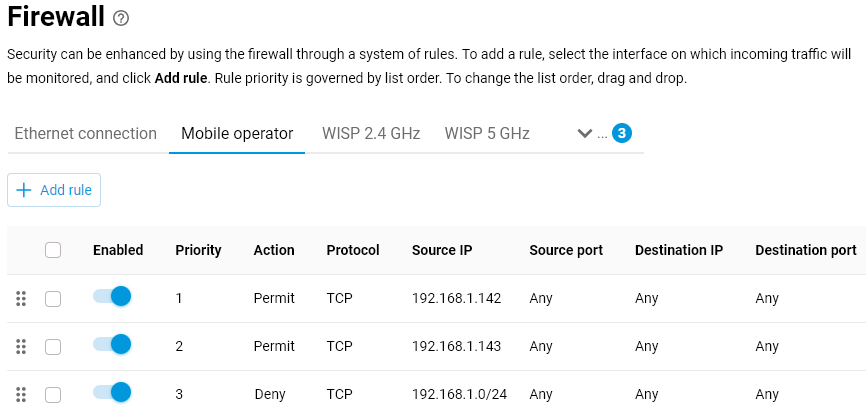
Below, we will look at an example of configuring a firewall on a router so that when switching to a backup connection, only specific network clients can access the Internet, while access is blocked for all others.
In the firewall settings, we need to create rules for the backup interface. In our example, a built-in 5G/4G/3G modem is used as the backup connection, but it could also be a USB modem. When connecting a 5G/4G/3G modem to the router, an interface of the UsbLte0 type is created by default (the name of the interface may vary depending on the type of modem being connected). On this interface, we will create three rules: two to grant access to client devices with IP addresses 192.168.1.142 and 192.168.1.143, and one rule to deny access to all other clients.
First, let's create an allow rule in which we specify the source IP address (the IP address of the client that will be allowed access) and the TCP protocol type.
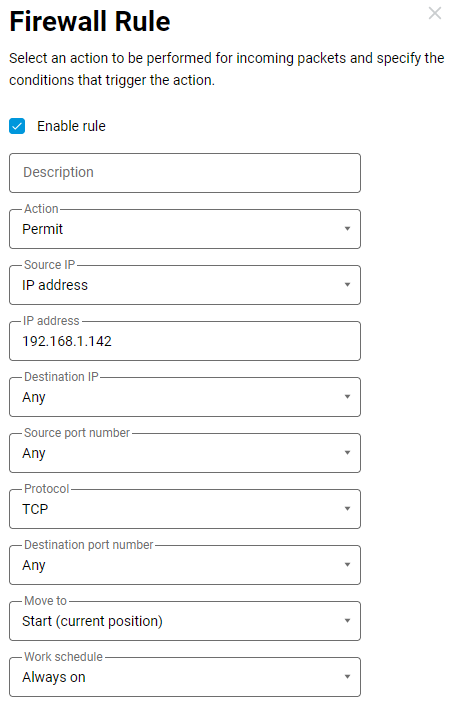
If you want to allow access to multiple network clients, create similar rules for them too.
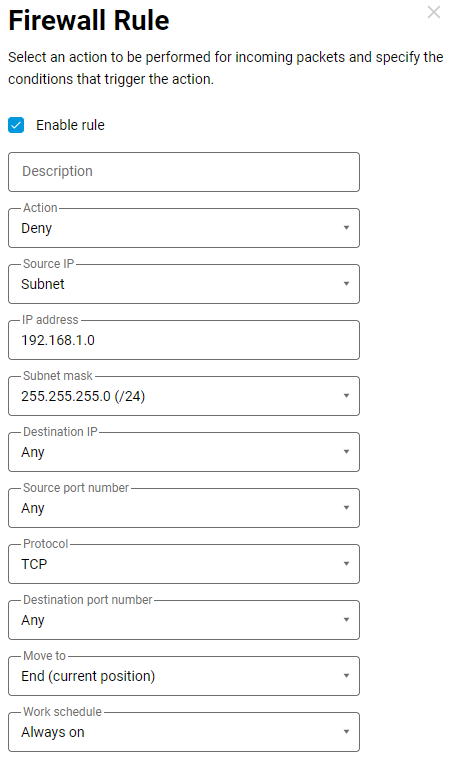
Then we create a blocking rule, specifying the subnet (192.168.1.0 with a mask of 255.255.255.0) as the source IP address and TCP as the protocol type.
Further setup is possible in two ways: by editing the router configuration file or from the router command-line interface (CLI).
Method 1. Editing the router configuration file.
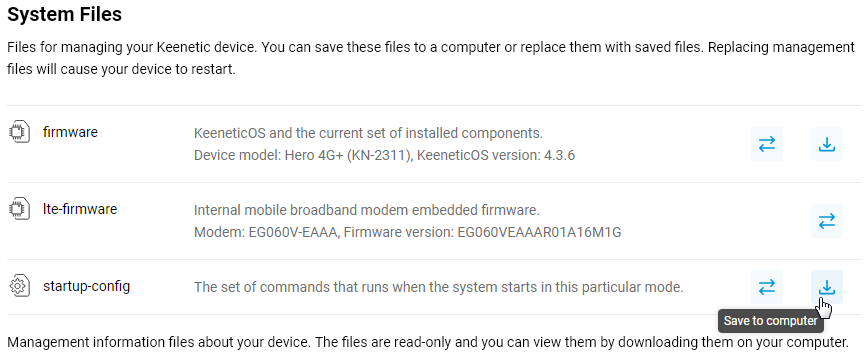
1.1 Go to the General System Settings page in the System Files section. Find the startup-config file. This is a text file with user settings that are executed when the router starts up. Save it on your computer for further editing.
Click on the startup-config file entry and then click Save to computer. The file will be downloaded by your web browser. If a file save window appears, specify the location (the folder where the file will be saved) and click Save or OK.
1.2 Open the startup-config configuration file in any text editor, such as Notepad. Then find the backup provider interface configuration section (in our example, this is UsbLte0) and replace the word in with out in the ip access-group line. Then save the file.
In our example, in the line
ip access-group _WEBADMIN_UsbLte0 inthe word in was replaced with out, resulting in the following line:
ip access-group _WEBADMIN_UsbLte0 out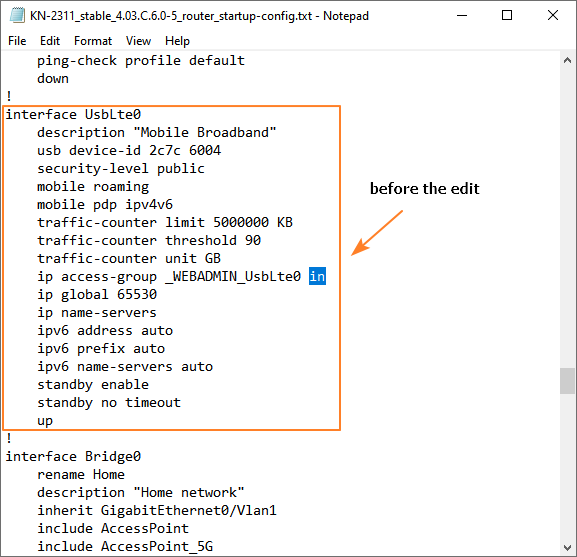
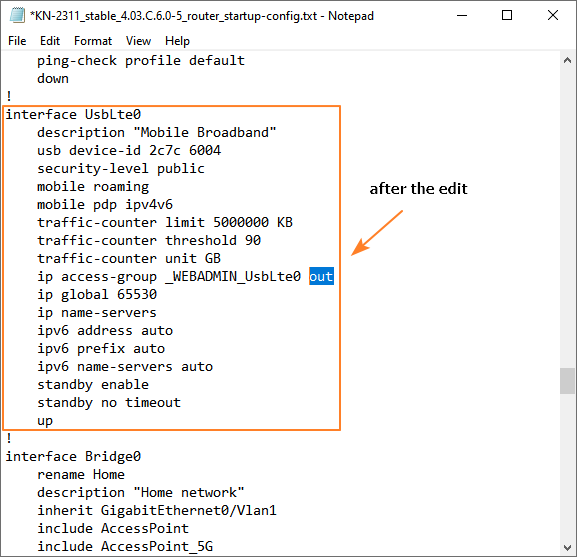
Be sure to save the changes to the file.
1.3 Now the edited startup-config system file needs to be written (uploaded) to the router. To do this, click the Replace file button and specify the path to the edited configuration file.

After uploading the startup-config file, the router will automatically reboot. Wait until the device is fully powered up.
Now, when the backup connection is activated, the router's firewall will only allow specific clients to access the Internet and will block access for the rest.
Method 2. Configuration from the router's command-line interface (CLI) or webcli.
The same configuration shown in Method 1 can be performed using commands.
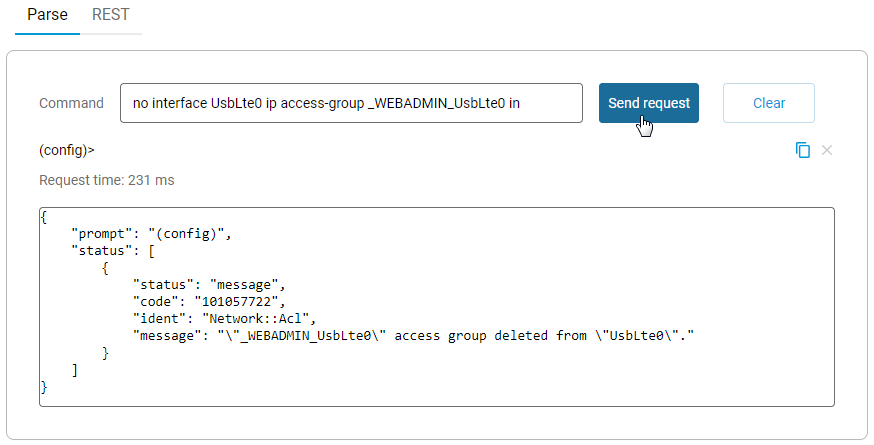
Connect to the command-line interface or webcli. First, execute the command:
no interface UsbLte0 ip access-group _WEBADMIN_UsbLte0 in
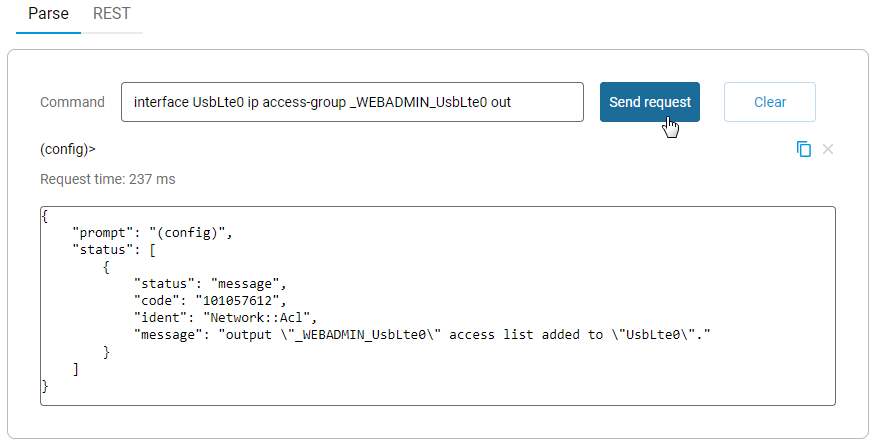
Then run the command:
interface UsbLte0 ip access-group _WEBADMIN_UsbLte0 out
The in and out parameter specifies the direction of traffic to which the ACL will be applied.
in — apply filtering to incoming packets
out — apply filtering to outgoing packets
To solve our problem, we need to set up filtering for outgoing network packets on the backup interface.
For more information, see the article How does a firewall work?
To save the settings, be sure to run the command:
system configuration save
For the full command syntax, see the command line interface reference guide in Download Center.